Beyond the Basics: A Roadmap to Different Types of AI
Introduction
Imagine this: for months, you have been struggling with joint pain, exhaustion, and odd symptoms. You go to Dr. Sharma, a pioneer in AI-powered diagnostics, feeling frustrated and anxious. Instead of large, cumbersome devices, her workspace is filled with sleek terminals that display sophisticated facial scans.
Dr. Sharma turns on the A.I. as you take a seat. Your face is analyzed by discreet cameras, which pick up minute micro-expressions that are hidden from view. The A.I. sorts through millions of medical photos and data points to find patterns. Suddenly, an unusual syndrome you have never heard of is displayed on the screen. Though slight, its facial symptoms exactly resemble yours.
You feel a surge of relief. At last, you have a solution and a place to begin your treatment. This is the potential of A.I. in healthcare—a ground-breaking technology that is expanding the parameters of diagnosis and giving hope to those who remain untreated.
This is how the magic of A.I. worked:
-
Image Recognition: Using an analysis of your face scan, the A.I. system finds subtle variations in skin texture, blood flow, and muscle movement. These seemingly unimportant features may indicate the presence of certain diseases.
-
Deep Learning: The A.I. detects these minute patterns and connects them to specific diagnoses after being trained on enormous databases of patient data and medical imagery. It's comparable to a lightning-fast and pinpoint detective going through a vast library of hints.
-
Personalized Diagnostics: A.I. can recognize distinct patterns concealed inside individual cases, unlike standard testing that frequently overlooks rare illnesses. This individualized approach allows early diagnosis and focused treatment even for the most mysterious conditions.
The objective of creating intelligent machines that are capable of thinking, learning, and acting on their own is at the core of artificial intelligence, a broad and rapidly developing discipline. It includes a range of tools and methods intended to provide machines with the ability to simulate cognitive functions, including perception, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making. Artificial intelligence systems may carry out tasks that usually require human intelligence by processing information, analyzing data, and adapting to their surroundings.
The Importance of A.I. in the current technological landscape.
Artificial Intelligence is quickly changing the globe and touching almost every part of human existence. Its influence can be seen in:
-
Transforming industries: A.I. drives innovation in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and transportation by automating activities and streamlining procedures.
-
Data Analysis: A.I. helps us with data and decision-making, increasing human potential. A.I. improves human capacities by helping us with data processing, decision-making, and fast and accurate jobs. It broadens our horizons and strengthens our skills.
-
Personalized experiences: Artificial intelligence customizes everything from product recommendations to delivering relevant news and entertainment to suit each user's requirements and preferences.
-
Scientific breakthroughs: A.I. analyzes large volumes of data, spots trends, and forecasts results in areas like medication development and climate change research, which speeds up scientific discoveries.
The emergence of artificial intelligence (A.I.) brings a new age in technological development and offers enormous promise for enhancing effectiveness, output, and well-being. It also brings up significant societal and ethical issues that need responsible response.
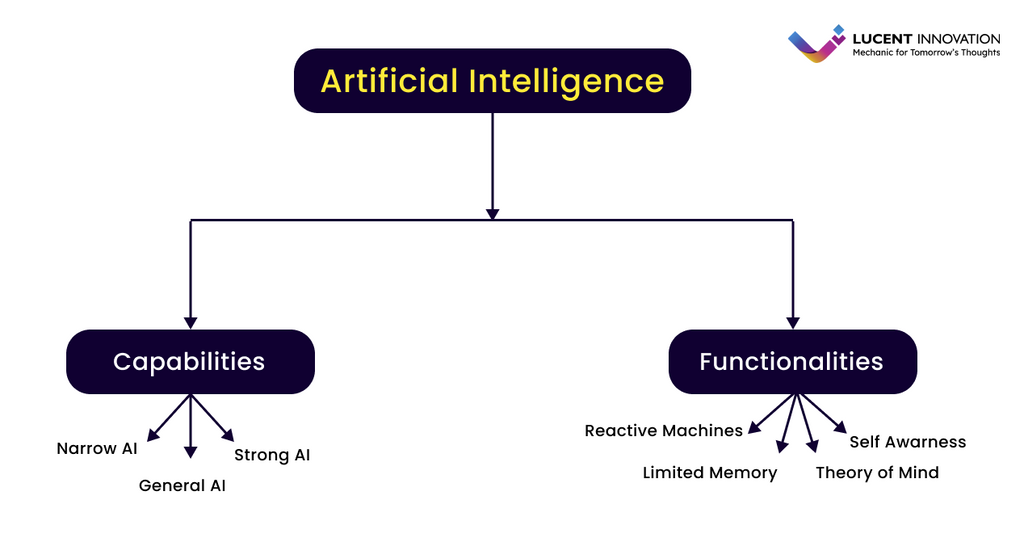
An overview of the multiple types of artificial intelligence
Discover the various kinds and uses of artificial intelligence as you investigate its broad spectrum. Each type of artificial intelligence (AI) has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, ranging from sophisticated neural networks inspired by the human brain to logic-driven rule-based systems.
We may organize AI into several categories according to various standards to gain a better understanding of its varied landscape:
Capability:
The term "artificial intelligence" (AI) based on capability describes the various types of intelligence that AI systems are capable of. Artificial intelligence capabilities are divided into several categories, from basic to advanced, based on the system's capacity to carry out tasks, learn, adapt, and display intellect comparable to that of people in particular fields.
-
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI): The foundation of AI, ANI is particularly good at specific tasks such as facial recognition and chess. Imagine it as an expert engineer with excellent proficiency in a single domain.
-
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): It is the peak of AI, able to perform any cognitive function that a person can. Imagine a multifaceted genius who can handle any task with ease. (It is under development)
-
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI): The ultimate mind-bending technology that is infinitely more intelligent than humans. Imagine it as an all-knowing being, able to accomplish things beyond our comprehension.
Types of Artificial Intelligence: Based on Functionality
The following four categories of AI can be applied to systems based on their performance.
Reactive Machines:
-
They are the most straightforward and earliest kind of artificial intelligence systems. They are reactive and don't base their decisions on recollections from the past.
-
Reactive machines comprise a computer system that analyzes its environment and responds accordingly.
-
Reactive machines consider the situation at hand before responding to it.
-
According to artificial intelligence expert Rodney Brooks, reactive machines are limited to the tasks given to them because they are unaware of their environment.
-
Google's AlphaGo and IBM's Deep Blue Systems are two examples of reactive machines.
Limited Memory:
-
Machines with limited memory can learn from past data to make decisions.
-
However, there is an immediate limit on how long users can access the data kept in the tiny memory.
-
Limited memory devices include chatbots, autonomous cars, and virtual assistants like Siri.
-
Self-driving cars make use of artificial intelligence with limited memory. It tracks other cars' current and historical movements surrounding a particular vehicle. The artificial intelligence machine's static data, which includes lane markers and traffic signals, is then supplemented with the acquired data.
-
This information can help a car in determining whether to change lanes or prevent a collision with another car. The goal of Mitsubishi Electric has been to advance this technology for autonomous vehicles.
Theory of Mind:
-
The theory of the mind interacts with the world via understanding people, animals, emotions, and objects.
-
This artificial intelligence is the least evolved of all the varieties. However, some scholars are working hard to create it.
-
Theory-of-mind and AI are real-world applications. Dr. Cynthia Breazeal, an MIT researcher, developed Kismet, a robot head, in the late 1990s. This robot head's ability to replicate and identify human emotions represents a significant technological advancement. Kismet, however, needs to be able to meet gaze or draw attention from others.
-
Sophia from Hanson Robotics is another example of artificial intelligence in action. Sophia can see thanks to the cameras in her eyes, which collaborate with computer algorithms. She maintained eye contact, identified people, and followed faces as a result.
Self-Awareness:
-
It is regarded as the highest point of artificial intelligence research.
-
Machines can have consciousness and self-awareness. Currently, no such devices are in use; thus far, this is only a theoretical idea.
-
Self-awareness A.I can understand its internal conditions, attributes, and states and see human emotions. This kind of artificial intelligence will enable machines to have their own feelings, needs, and beliefs in addition to understanding and evoking emotions in people with whom they interact.

What direction will Artificial Intelligence take in the future?
The story around Dr. Sharma and AI-powered diagnostics only scratches the surface of this technology's revolutionary possibilities. A significant issue remains as we explore the complex world of artificial intelligence: how will AI affect our future?
However, enormous power includes considerable responsibility. We must continue to be careful caretakers of AI progress as we release its potential. Ethical issues, justice, and human oversight are essential to guarantee that AI benefits humanity rather than the other way around.
So, the question we face isn't "if" AI will change the world, but "how" we will guide this change.
FAQ's
1.What are the types of A.I?
Artificial intelligence can be broadly divided into two categories: narrow AI and general AI. While comprehensive artificial intelligence (AI), commonly referred to as artificial general intelligence (AGI), has not yet been attained and attempts to imitate human intelligence in all fields, narrow AI is focused on activities.
2.Can AI help me in giving my consumers personalized product recommendations?
It's true that machine learning may evaluate browsing patterns and past purchases to make appropriate product recommendations that boost satisfaction and conversion rates.
3.How can order fulfillment and inventory management be automated using AI?
By handling repetitive activities, anticipating demand, and optimizing stock levels, machine learning and robotics can save time and resources.
4.Is it possible to fight fraudulent transactions with AI?
By spotting questionable trends in transactions, machine learning can assist stop fraud and safeguard consumer information.
5.How can software testing and bug discovery be automated using AI?
Compared to manual testing, Deep Learning is faster and more efficient in analyzing code and spotting possible problems.
6.Can AI help with performance optimization and network troubleshooting?
By identifying and forecasting issues through the analysis of network data, machine learning can guarantee uninterrupted operation and reduce downtime.
7.How might AI improve cybersecurity?
Cyberattacks can be quickly detected and responded to by machine learning, shielding data and systems from unwanted access.
8.Can artificial intelligence optimize energy use and cut expenses?
To maximize energy production and distribution, machine learning may evaluate meteorological data, energy consumption trends, and equipment performance.
9.How can artificial intelligence be applied to equipment and power grid predictive maintenance?
A dependable energy supply may be ensured, and downtime can be avoided by using machine learning to detect possible issues before they happen.
10.How can AI help medical professionals diagnose conditions and choose the best course of treatment?
To offer insights and facilitate well-informed decision-making, Deep Learning can evaluate patient data and medical imaging.
11.Can artificial intelligence increase efficiency in healthcare facilities by automating administrative tasks?
Chatbot technology and natural language processing can both automate the transcription of medical records and respond to patient questions, saving up staff time for patient care.
12.How can AI improve patient outcomes and tailor treatment schedules?
By analyzing unique patient data, machine learning can foresee dangers and customize treatment regimens, improving patient outcomes.
Also Read, The History of Artificial Intelligence: A Detailed Guide
